Ever hear of Alopecia Areata? It affects more people than you think.
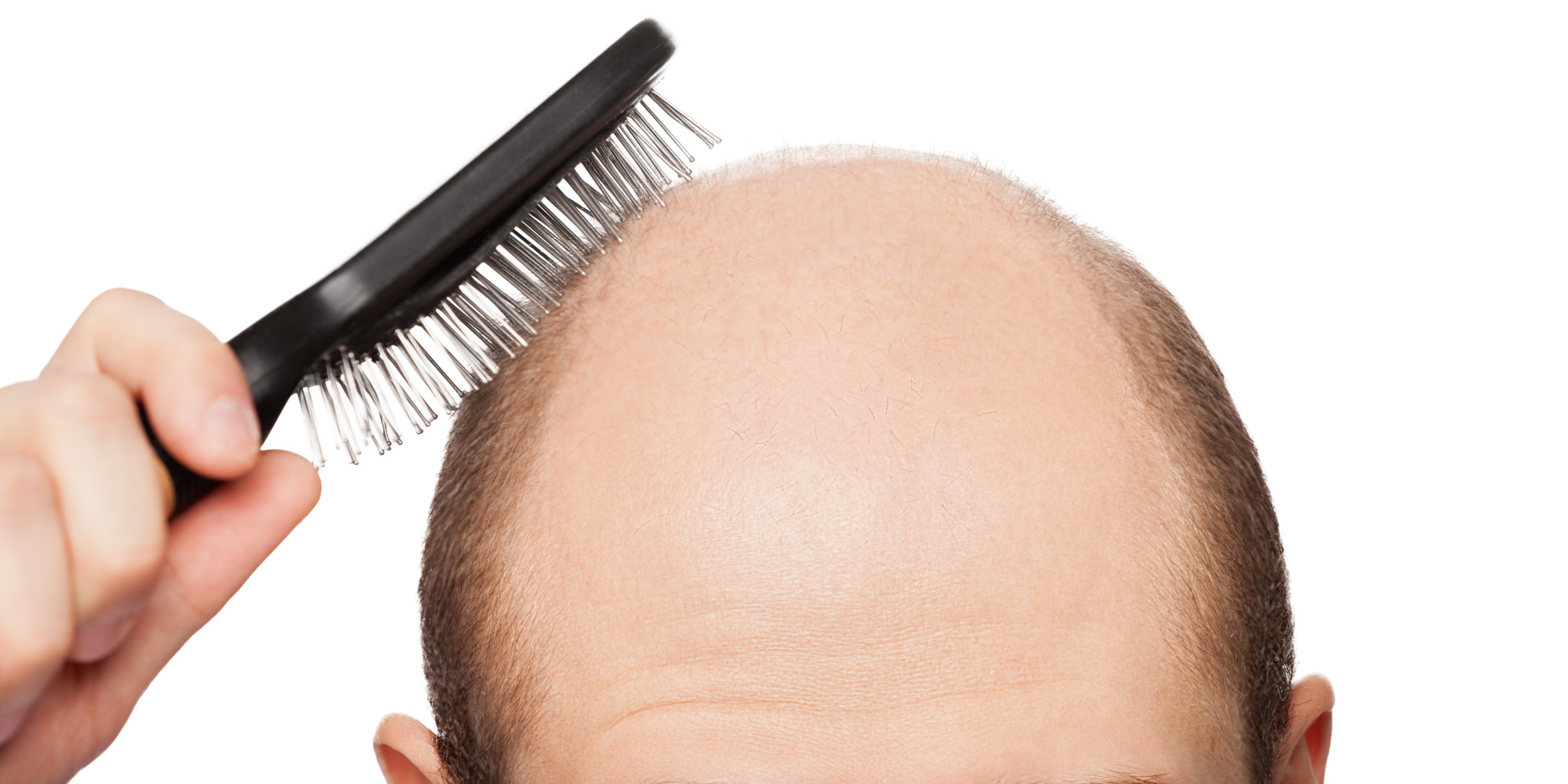
Alopecia is the fancy term for “hair loss”, and it’s used to describe all the various reasons why your hair is falling out. There are a number of types of alopecia, but one of the worst is known as alopecia areata. This, simply put, is an autoimmune disorder that causes your body to attack itself. Your immune system ends up attacking the hair follicles, damaging them and leading to hair loss.
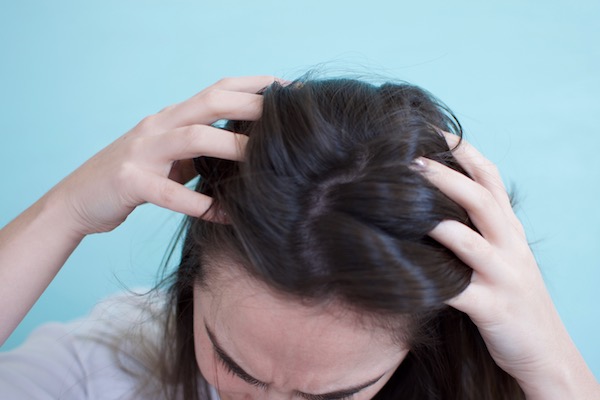
Your hair may begin to fall out one at a time, or you may start to notice large clumps of hair going missing all at once. Often, the clumps of hair that you lose will start out around the size of a quarter, but they will grow as more and more of your hair follicles shut down due to the autoimmune disorder.
Of course, if the disorder goes unchecked, you may begin to lose hair in places other than your head. This is known as alopecia areata universalis, and it involves hair loss all over your body–chest hair, back hair, pubic hair, eyebrows, and so on. If you only lose all the hair on your head, this is known as alopecia areata totalis.
But what are the causes of alopecia areata? What is causing your body to attack itself in the first place?
Sadly, it’s not exactly know what the causes of alopecia areata are. Autoimmune disorders are difficult to predict, and they can affect anyone, anywhere, and at any time. There are no specific factors that contribute to your developing alopecia areata. If someone in your family has developed the hair loss, it’s slightly more likely that you will too. However, even if you don’t have a history of alopecia, there is still a very real chance that you can develop it.

READ MORE: 11 Ways to Increase Scalp Circulation
One interesting thing to note: people with a family history of autoimmune disorders (including thyroid problems, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or diabetes) will have a higher chance of developing alopecia areata. Their bodies are already prone to attacking healthy cells thanks to the various disorders, so there is a much higher risk that the body will also view hair follicles and the hair growing there as invaders to be eliminated.
But what can you do about alopecia areata? If you can’t figure out the causes of alopecia areata, is there anything you can do to prevent or deal with it?
The bad news is that there is no “cure” for alopecia areata. The good news is that you can regrow your hair with the proper treatments. There are a number of drugs that can help you to deal with the problem, including:
- Rogaine — This topical drug is popular among those dealing with pattern baldness, and it can help to deal with alopecia areata as well. It may take up to 12 weeks of using Rogaine before you see results, but it can lead to some (albeit not a lot) of hair regrowth.
- Corticosteroids –– These drugs are often recommended to deal with the inflammation that results from autoimmune diseases. Your body will respond slowly to the treatment, but it can help to slow down and potentially even stop the hair loss.
- Topical contact sensitizers or allergens –– These topical treatments promote inflammation, which may possibly lead to hair regrowth. This is also known as topical immunotherapy–essentially treating your immune system in that specific region.
But you need to realize that, even with these drugs, there’s no guarantee that your hair will grow back. Alopecia areata may be impossible to reverse, meaning it’s time to shave your head and embrace your inner bald person!